How Will the Action Potential at R1 Change as You
The action potential didnt change as the stimulus voltage increased. In the presence of lidocaine the action potential was NOT affected at R1 because _____.
Background Biphasic Extracellular Recording
The effects of lidocaine and tetrodotoxin were _____.
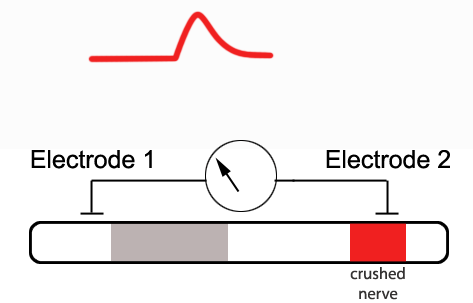
. At the axon terminal each action potential causes the release of neurotransmitter. A nerve is _____. Select View Experiment Results if you need to review your results from the Experiment to answer a question Action Potential Stimulus Voltage mv 10 Peak Value at R1 LV 0 Peak Value at R2 PV 0 100 No Yes 20 30 100 100 100 Yes 40 100 Yes 100 100 50 100 Yes.
The action potential didnt change as the stimulus voltage increased. This is because once threshold is met the event is all or none not graded. The action potential will not change.
This neurotransmitter diffuses to the receiving end of an interneuron where it binds to receptors and causesshow more content Why is there a larger depolarizing response at R1 when you apply a moderate intensity stimulus. In the presence of lidocaine the action potential was NOT affected at R1 because lidocaine was applied downstream of R1. The duration of the action potential will decrease.
This anesthetic power allows the ionic fluxes capable of stimulating impulses to be diffused and this allows a dormancy to be achieved. Similar but tetrodotoxin had a greater effect. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication.
Threshold is the only point and action potential is fixed whenever it occurs. How did the action potential at R1 or R2 change as you increased the stimulus voltage above the threshold voltage. Identify the type of membrane potential graded receptor potential or action potential that occurred at R1 R2 R3 and R4 when you applied a moderate stimulus view Experiment Results to view the response to this stimulus.
The action potential will not change. The action potential at R1 or at R2 did not change as the stimulus voltage was increased above the threshold voltage. The action potential had to propagate from R1 to R2.
How did the action potential at R1 or R2 change as you increased the stimulus voltage above the threshold voltage. The time between the stimulation and the action potential at R1 differed for each axon because the axon diameter and amount of myelination varied for each axon. An action potential is an all-or-nothing event.
An increase in extracellular K would depolarize a neuron. An action potential is an all or nothing event. How did the action potential at R1 or R2 change as you increased the stimulus voltage above the threshold voltage.
From what you have just learned about generating an action potential what effect would this have on nearby axons. The initiation of an action potential in a sensory neuron in the body normally. An action potential is an all-or-nothing event.
A bundle of axons. The action potential had to propagate from R1 to R2. Identify the type of membrane potential graded receptor potential or action potential that occurred at R1 R2 R3 and R4 when you applied a moderate stimulus.
4An action potential is an all-or-nothing event. 2 An increase in extracellular K would depolarize a neuron. An action potential was always seen at R1.
The velocity changes so when it gets very slow you. Action potential didnt change as the stimulus voltage increased. The peak value of the action potential will increase.
Why did you need to change the timescale on the oscilloscope for each axon. Lidocaine was applied downstream of R1. How well did the results compare with your prediction.
How will the action potential at R1 or R2 change as you continue to increase the stimulus voltage. An action potential is defined as a sudden fast transitory and propagating change of the resting membrane potential. This article will discuss the definition steps and phases of the action potential.
An action potential is usually initiated in an axon at or near. What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in Figure 1257. This is because once threshold is met the event it all or none not graded.
The change in the membrane voltage from -70 mV at rest to 30 mV at the end of depolarization is a 100-mV change. The peak value of the action potential will increase. This depolarization would occur if neurons were damaged.
These results compare with my prediction that there would be no change in potential. When you applied a moderate stimulus to the sensory receptor a larger depolarizing response occurred at R1 and an action potential was generated at R2 and at R4. 22 rows How did the action potential at R1 or at R2 change as you increased the stimulus voltage.
Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of generating an action potential. How well did the results compare with your prediction. Lidocaine is an anesthetic that has the power to neutralize neuromal membranes.
That property is called the excitability. Page 2 of 4If a graded receptor potential made the resting membrane potential of the axon more negative for example -70 mV changes to -75 mV you would expect2. Predict Question How will the action potential at R1 or R2 change as you continue to increase the stimulus voltage.
In the presence of lidocaine the action potential was NOT affected at R1 because _____. How well did the results compare with your prediction. All of the above.
When you applied a moderate stimulus to the sensory receptor a larger depolarizing response occurred at R1 and an action potential was generated at R2 and at R4. The peak value of the action potential will increase. By the first recording electrode R1.
A action potential propagation is in one direction B lidocaine was applied upstream of R1 C lidocaine doesnt have an effect on the generation of action potentials D there are no voltage-gated sodium channels to be affected. This is necessary in order to see the action potentials. Follows a sufficiently large depolarizing receptor.
Identify the type of membrane potential graded receptor potential or action potential that occurred at R1. Graded receptor potential at R1 and R3 with APs at R2 and R4.
Conduction Velocity Difference And Absolute Methods
New Hinton Nature Paper Revisits Backpropagation Offers Insights For Understanding Learning In The Co Nature Paper Artificial Neural Network Learning Problems
Physio Ex Exercise 3 Activity 3 Physioex Lab Report Exercise 3 Neurophysiology Of Nerve Impulses Studocu

Belum ada Komentar untuk "How Will the Action Potential at R1 Change as You"
Posting Komentar